8. This is just the rate of change of the radius with angle. For instance, if you describe a circle, you would expect this derivative to be zero, since the radius does not change with angle, and this is seen by f(θ) = R f′(θ) = 0 f ( θ) = R f ′ ( θ) = 0. The tangent to the curve can be calculated as follows.. Calculate. −x 2y dx + 2 xy dy, where C is the circle of radius 2 centered on the origin. C. Answer: Green's theorem tells us that if F = (M, N) and C is a positively oriented simple closed curve, then.
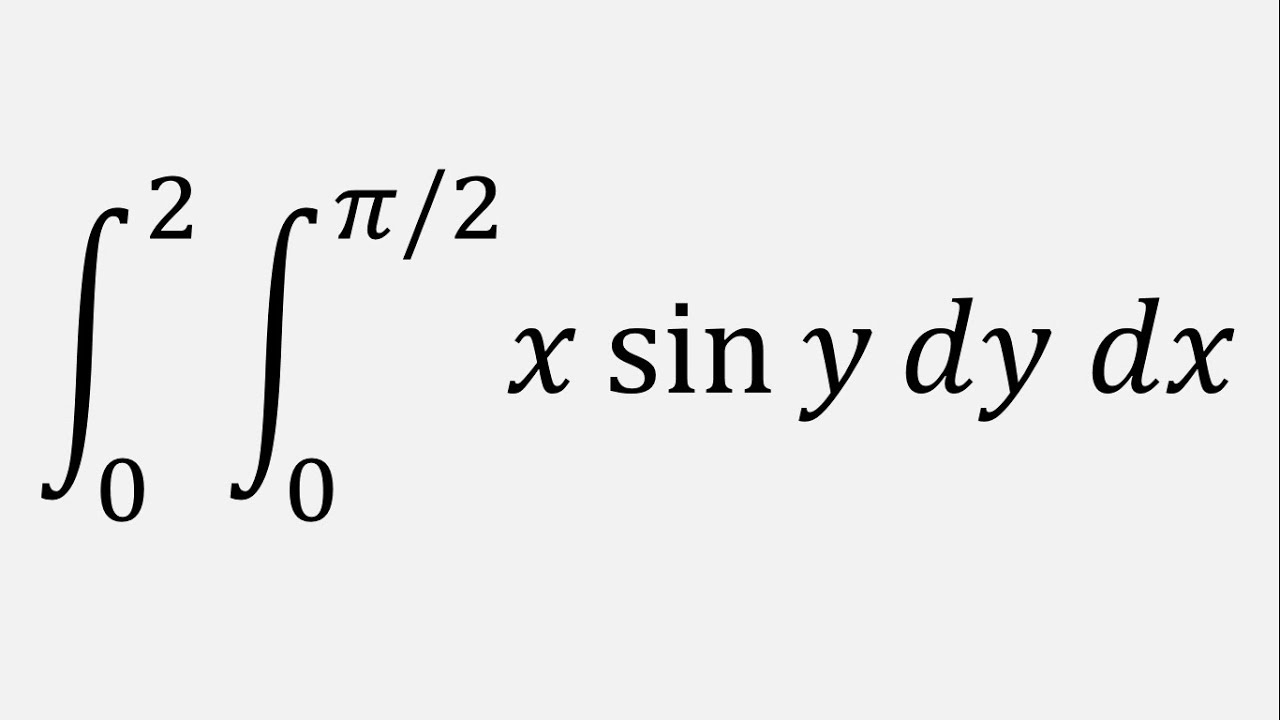
Double Integral x sin y dy dx , y = 0 to pi/2 , x = 0 to 2 YouTube

Example 33 Find dy/dx, if yx + xy + xx = ab Class 12

What is the Difference Between dy/dx and d/dx YouTube

dr/dθ+r*sec(θ)=cos(θ) ;Ecuación diferencial lineal, método concreto, con sol. homogénea y

Geneseo Math 222 01 Polar Coordinate Derivatives
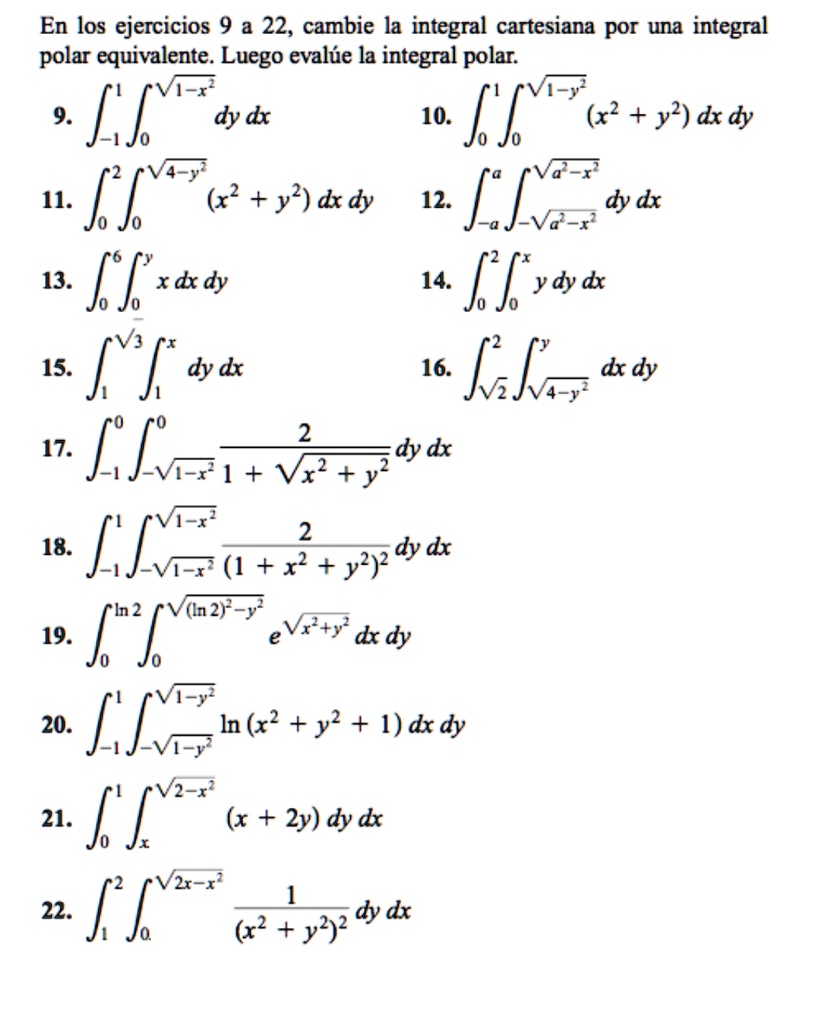
SOLVED En los ejercicios 9 y 22, cambie la integral cartesiana por una integral polar
![[Physics] Derivation of d\theta = ds/r Math Solves Everything [Physics] Derivation of d\theta = ds/r Math Solves Everything](https://i.stack.imgur.com/vEEJN.jpg)
[Physics] Derivation of d\theta = ds/r Math Solves Everything

Shorts Cartesian to Polar 𝒅𝒙 𝒅𝒚 = 𝒓 𝒅𝒓 𝒅𝜽 YouTube

Ex 5.3, 3 Find dy/dx in, ax+by2 = cos y Chapter 5 NCERT
[Solved] How to prove dxdy = r dr d \theta? 9to5Science

double integration polar coordinates r dθ dr GeoGebra
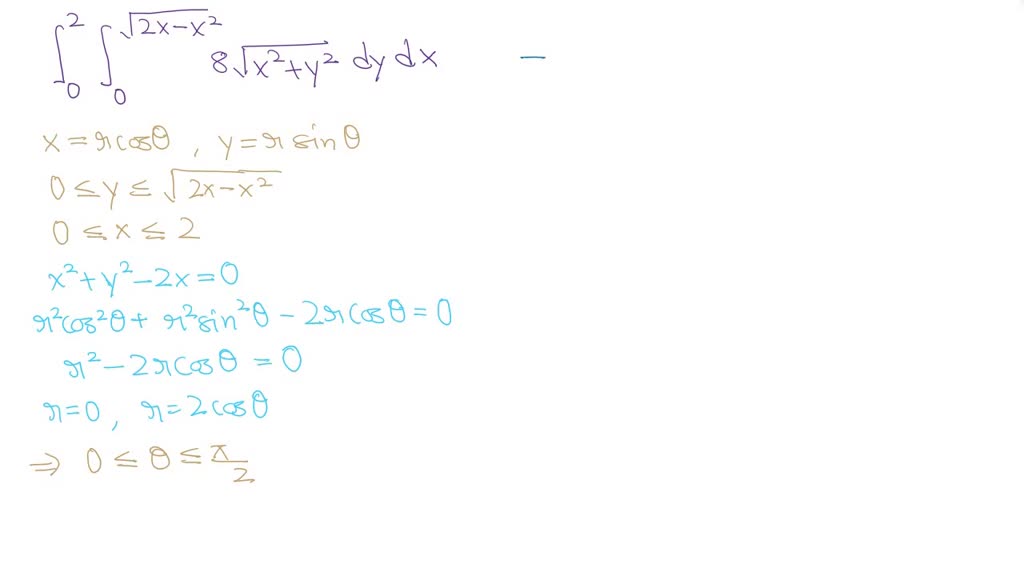
SOLVED Evaluate the iterated integral by converting to polar coordinates 2x X2 8V x2 + y2 dy
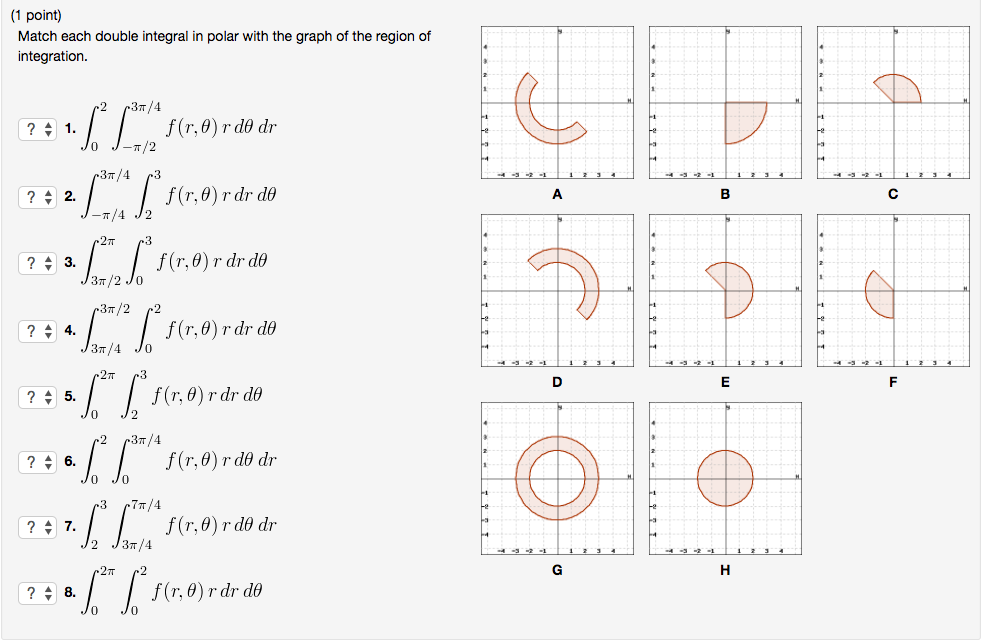
Solved (1 point) Match each double integral in polar with
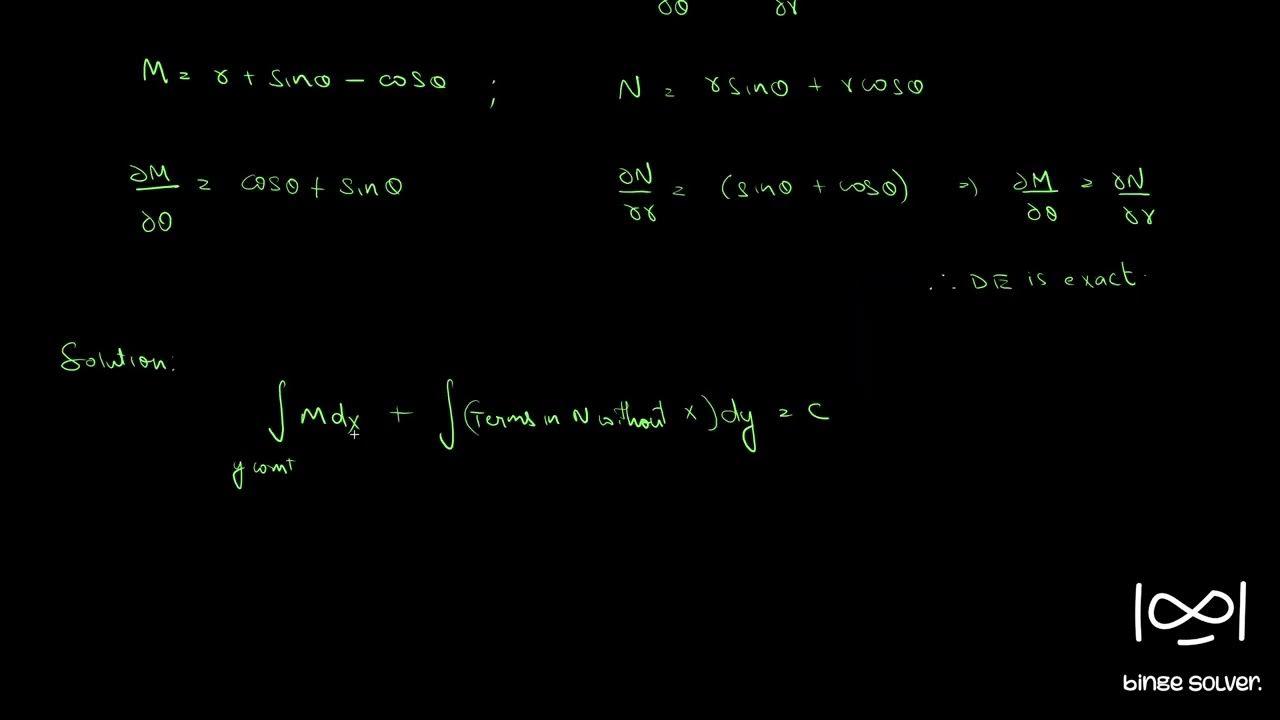
Q165 Solve (r+sinθ cosθ)dr + r(sinθ + Cosθ)dθ = 0 YouTube
[Solved] how to get dx\; dy=r\;dr\;d\theta 9to5Science

derivatives How dxdy rdrd\theta during integration by substitution with polar

Find dy/dx given Parametric Equations x = sin^2(theta), y = cos^2(theta) YouTube

r 2 π r sinθ r dr dθ dθ r= PDF

proof verification Transform dx/dt to dr/dt polar coordinates Mathematics Stack Exchange

DOUBLE INTEGRAL Evaluate ∫∫ r dr dθ YouTube
Practice 1: When r is given by a formula we can calculate dy/dx , the slope of the tangent line, by using the polar-rectangular conversion formulas dy dy dx and the Chain Rule. By the Chain Rule dθ = dx dθ , so we can dy dx solve for dx by dividing each side of the equation by dθ . dθ dx. dθ.. Example 15.7.3: Setting up a Triple Integral in Two Ways. Let E be the region bounded below by the cone z = √x2 + y2 and above by the paraboloid z = 2 − x2 − y2. (Figure 15.5.4). Set up a triple integral in cylindrical coordinates to find the volume of the region, using the following orders of integration: a. dzdrdθ.